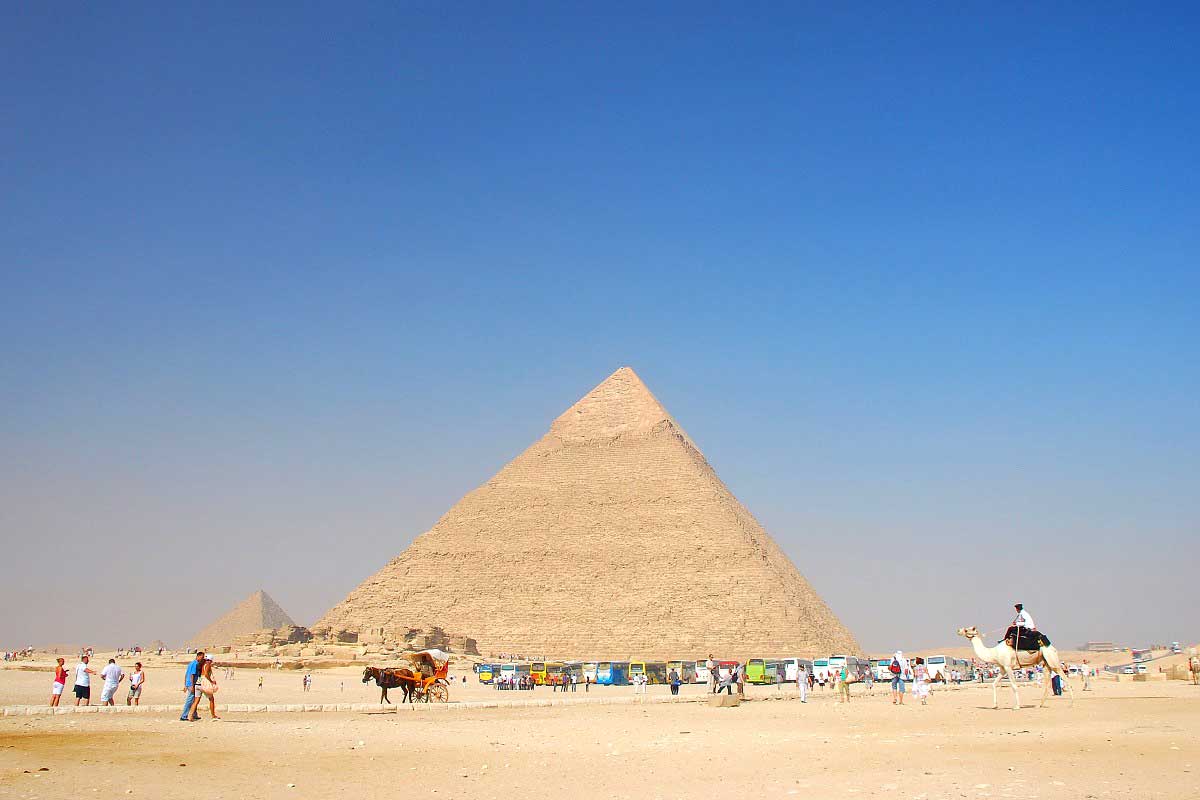
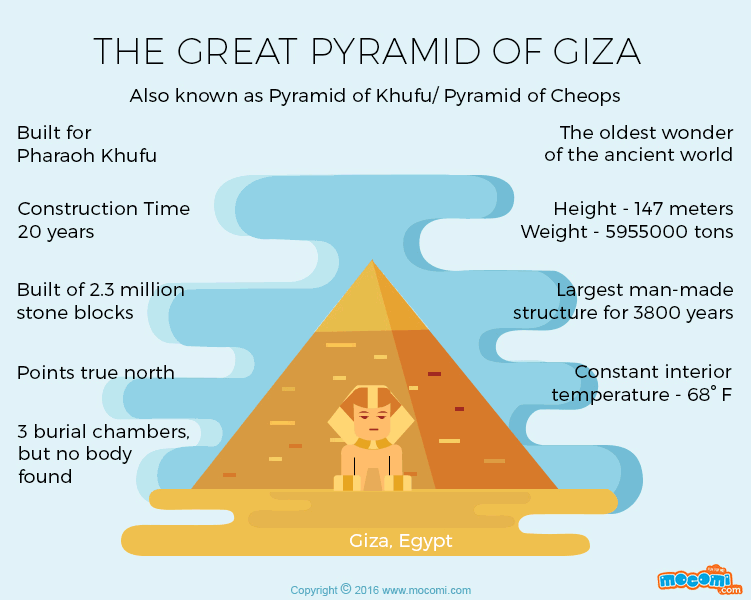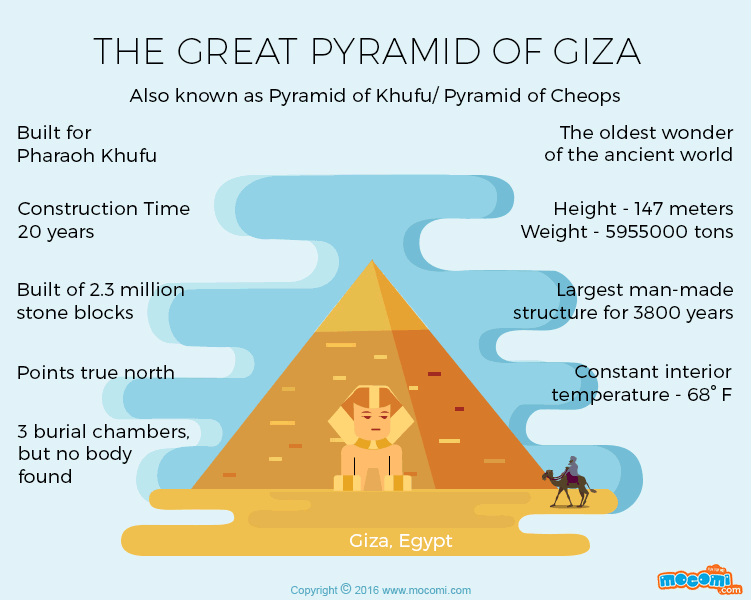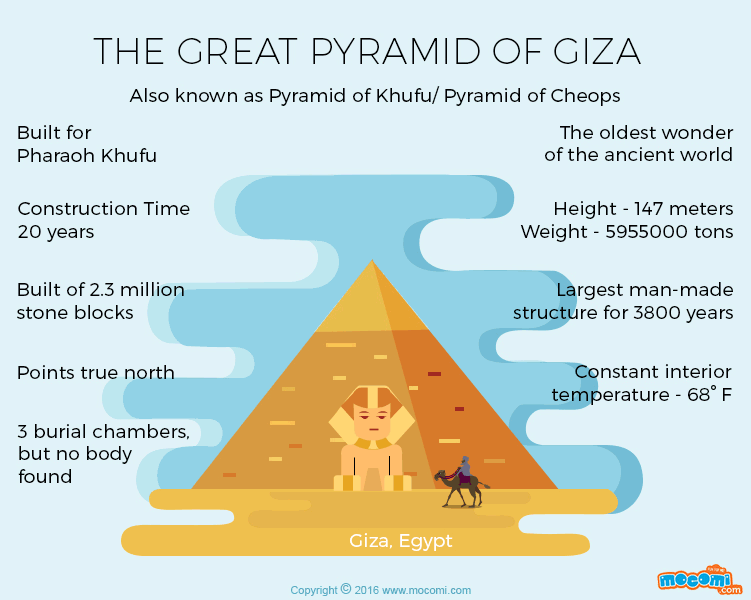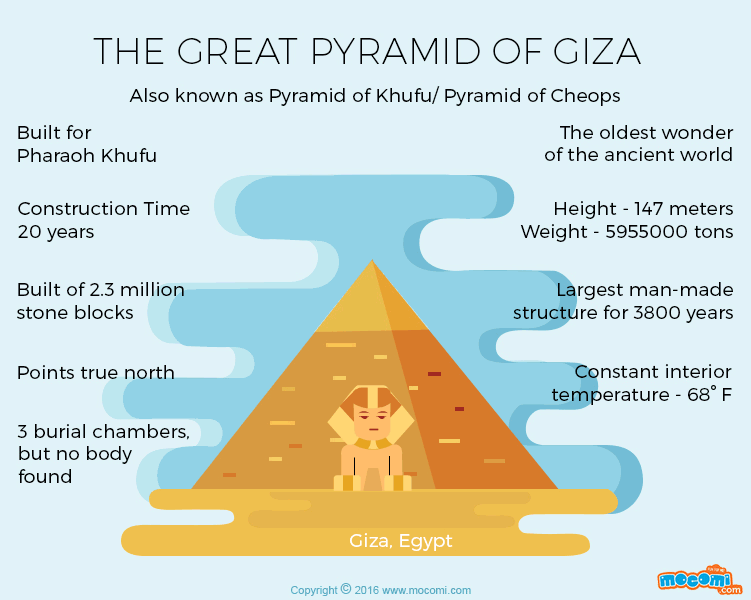
The Great Pyramid of Giza, also known as the Pyramid of Khufu or the Pyramid of Cheops, is an architectural masterpiece that rightfully claims its position among the illustrious Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. Situated on the storied Giza Plateau, the Great Pyramid of Giza facts, a mere stone’s throw away from the bustling city of Cairo, Egypt, this monumental structure has captivated the imagination of humanity for millennia. You may love to know about the history of Latin America.
Erected during the reign of Pharaoh Khufu, often affectionately referred to as Cheops, during the esteemed Fourth Dynasty of Egypt’s venerable Old Kingdom, the genesis of the Great Pyramid unfolded between the years 2580-2560 BCE. Initially conceived as the grand sepulcher for the revered pharaoh, it once soared to unparalleled heights, reigning supreme as the tallest and eldest sibling among the trio of pyramids adorning the Giza Plateau. At its zenith, it reached an astonishing altitude of 146.6 meters (481 feet). Yet, the relentless march of time witnessed the gradual removal of its outer casing stones, which gradually eroded its stature to approximately 138.8 meters (455 feet). Women travel must-haves.
Journeying into the very heart of the Great Pyramid unveils an intricate subterranean world, replete with chambers and passageways—an enigmatic labyrinth in its own right. Noteworthy among these cryptic recesses are the King’s Chamber and the Queen’s Chamber, each shrouded in their own layers of mystery. It is within the sacred precincts of the King’s Chamber that one encounters a resplendent red granite sarcophagus, meticulously designed to enshroud the earthly remains of the venerated pharaoh.
Yet, one of the most enduring riddles enveloping the Great Pyramid is its meticulous alignment with the cardinal points of the compass—an intricate enigma that alludes to the ancient Egyptians’ profound grasp of astronomy and mathematics. The precise orientation of the pyramid stands as a resounding testament to their astronomical acumen, with its sides aligning almost faultlessly with the cardinal directions. Traveloka: Southeast Asia’s Leading Travel Platform. Best prices for hotels, flights, buses, trains, & attractions
The sheer magnitude and precision embedded within the structure of the Great Pyramid are nothing short of awe-inspiring. Comprised of an astounding 2.3 million monumental blocks hewn from limestone and granite, with each colossal block weighing several tons, the construction methods employed in this mammoth endeavor persist as a profound enigma, igniting the intellectual curiosity of scholars and visionaries across the epochs. An intriguing supposition posits that the ancient Egyptians orchestrated a symphony of colossal ramps, ingenious levers, and a formidable workforce of adept artisans to materialize this monumental achievement. Learn more about the 8 wonders of the ancient world.
Great Pyramid of Giza facts
Across the pages of history, the Great Pyramid has exerted an indomitable magnetic pull, drawing intrepid explorers, erudite scholars, and curious wanderers from the farthest corners of the globe. A kaleidoscope of theories regarding its origins and purpose has unfurled, spanning a vast spectrum from the notion of it serving as an astronomical observatory to symbolizing the eternal cycle of life. The great pyramids aimed at establishing the tomb of the dead Pharaoh were the places where the pharaohs began their new journey into the afterlife. To find out more, let’s read some more amazing and interesting Great Pyramid of Giza facts:
Ancient Marvel of the World
The Great Pyramids of Giza, standing as iconic symbols of Egypt’s ancient civilization, are the oldest among the wonders of the world. Their construction commenced around 2500 BC during the early dynasties of Egypt, marking an era when the foundations of this remarkable civilization were being laid. These towering structures, comprised of millions of precisely cut stones, served as monumental tombs for pharaohs, reflecting the spiritual and cultural significance of the time. Qatar Airways: Book a ticket and fly with confidence all over the world
A Place Among the Seven Wonders
In the ancient world, spanning from the third millennium BC to the third century BC, the Great Pyramid of Giza held a distinguished position as one of the seven wonders. This architectural marvel, a testament to the ingenuity of its builders, took approximately two decades to complete. As a testament to human craftsmanship and engineering, these pyramids showcased the mastery of ancient Egyptian architects and laborers who toiled tirelessly to create these monumental structures.
An Unrivaled Marvel for Millennia
Archaeological records indicate that the Great Pyramid of Giza held the title of the world’s tallest man-made structure for an astounding 3,800 years. Its towering presence remained unparalleled, a symbol of human achievement and engineering prowess for centuries on end. The enduring grandeur of these pyramids, with their precisely aligned dimensions and celestial significance, continues to captivate and inspire people worldwide, highlighting their enduring legacy. AirHelp: Helps passengers receive up to €600 in compensation for delayed or canceled flights
Base Is Square
The Great Pyramid’s base boasts remarkable geometric precision as it forms a perfect square. Each side of this square measures approximately 756 feet, and the expansive base covers an area equivalent to 13 acres, with ample space to accommodate about 10 football or soccer fields. This level of geometric precision and alignment is a testament to the meticulous planning and architectural expertise of the builders.
203 Steps to the Top
Ascending to the pinnacle of the pyramid is no small feat, as it involves climbing a staggering 203 steps to reach the summit. The precise measurement and mathematical precision involved in the construction of the pyramid, including its internal passages and chambers, are indicative of the advanced mathematical and architectural knowledge possessed by the ancient Egyptians. Qeeq: Fast-growing car rental platform, listing over 7 million rental cars in ~200 countries
How Did They Make It?
The construction of such an immense structure without modern machinery or technology is a testament to the remarkable skills and ingenuity of ancient Egyptian builders. They lacked the machinery we take for granted today, including cranes, trucks, electric saws, and even electricity. Moreover, they relied on copper, a relatively soft metal, instead of iron for their tools, and they did not possess the wheel as we know it. These facts underscore the remarkable craftsmanship and dedication of the labor force that built these monumental structures.
Inside the Pyramid
Within the Great Pyramid, a labyrinthine network of tunnels and chambers unfolds. The pyramid’s interior features a range of architectural marvels, including the Queen’s Chamber, the King’s Chamber, the Grand Gallery, and the Air Shaft, each serving its own enigmatic purpose. These inner sanctums provide a glimpse into the sophisticated design and purposeful construction of the pyramid, fueling intrigue and fascination among those who explore its depths. Aviasales: A trusted service for buying flight tickets from reliable agencies at the lowest possible rates
Slight Curvature
One distinctive characteristic of the Great Pyramid of Giza is its slight curvature. Unlike the common perception of pyramids as perfectly angular structures, the Great Pyramid features subtle convexities in its geometry. This architectural choice, whether deliberate or a result of the construction process, adds to the enigmatic allure of this ancient wonder, inviting speculation about its significance and purpose.
The Pyramids Are Contracting
Over the millennia, the Great Pyramid of Giza has undergone changes, including a gradual reduction in its original height. Standing at an impressive 481 feet or 146.5 meters in antiquity, the pyramid has experienced erosion and weathering over thousands of years, resulting in a reduction in height. Today, it stands at approximately 455 feet or 138.8 meters. This ongoing transformation serves as a testament to the enduring nature of these ancient structures and the passage of time. Tiqets: Directly bookable and instantly available mobile tickets for attractions around the world
The Stones Are Heavy
The construction of the Great Pyramid required an astonishing number of stones, exceeding two million in total. These colossal stone blocks vary in weight from 2 to 30 tons, with some blocks surpassing 50 tons in mass. The logistics of quarrying, transporting, and precisely positioning these immense stones represent a remarkable feat of engineering and organization by the ancient builders. The sheer magnitude of these stones adds to the mystique and wonder surrounding the Great Pyramid of Giza and the incredible achievements of the pyramid’s architects and labor force.
Skilled Labor Behind the Construction
Historical accounts and archaeological findings suggest that more than 20,000 skilled workers, including stone craftsmen, architects, engineers, surveyors, builders, and various artisans, were instrumental in the construction of the Great Pyramid of Khufu. The organization and coordination required for this colossal undertaking reveal not only the sheer scale of the workforce but also the central role of skilled labor in transforming the grand vision of the ancient Egyptians into reality. Compensair: A service that helps customers receive compensation for flight delays, cancellations, or denied boarding
The Lion with a Human Head
Adjacent to the pyramids lies a remarkable structure known as the Great Sphinx, a statue depicting a lion with a human head. Often referred to simply as the Sphinx or the Sphinx of Giza, this colossal figure holds profound significance in Egyptian mythology. Comprising the body of a lion and the head of a human, the Sphinx is a mythical creature that has captured the imagination of countless generations. It stands as a sentinel guarding the ancient necropolis, embodying the rich tapestry of beliefs and symbols that defined ancient Egyptian culture.
Divided Across East and West Fields
The Giza Plateau encompasses two significant areas associated with the pyramids: the Giza West Field, situated to the west of the Khufu Pyramid, and the East Giza Field, positioned in front of the Khufu Pyramid. These fields represent important aspects of the Giza Pyramid Complex, offering additional insights into the historical and architectural significance of this timeless wonder.
While the West Field hints at the organizational aspects of pyramid construction and the lives of those involved, the East Field stands as a testament to the grandeur and mystique of the pyramids’ exteriors, drawing countless visitors and scholars to explore their enduring mysteries. Hotellook: A platform for comparing hotel prices around the world (250,000 properties in 205 countries)
The Giza Pyramid Complex: A Remarkable Ensemble
The Giza Pyramid Complex is not limited to the singular Great Pyramid; it encompasses a trio of impressive pyramids, namely Khufu (also known as Sheps), Khafre (or Chefren), and Menkaure (alternatively, Makirinos). Nestled within this expansive complex are also the enigmatic Great Sphinx, numerous burial sites, a bustling village, and an industrial complex.
Among these, the Great Pyramid of Giza, originally known as Khufu’s Horizon, stands as the largest and most iconic of them all. Legend attributes its construction to the Egyptian Pharaoh Khufu. The Khafre Pyramid, the second-largest in the ensemble, also adds to the grandeur of this ancient marvel.
A New Journey in the Afterlife
The construction of these monumental pyramids served a profound purpose—to serve as the final resting places for the Pharaohs of Egypt who once ruled over the vast Egyptian kingdom. In the rich tapestry of ancient Egyptian belief systems, death marked the beginning of a new journey, and these pyramids were meticulously designed to facilitate this transition. i’way: Private car service to and from 600 airports worldwide
It was firmly believed that in the afterlife, the Pharaohs would require all the necessities they enjoyed in life. Consequently, their tombs were filled with a treasure trove of important items and treasures, all carefully interred alongside the deceased rulers. This tradition of equipping the deceased Pharaohs with items for the afterlife continues to captivate and fascinate observers to this day, underscoring the deep spiritual and cultural significance of the pyramids.
No Records Found
One of the most intriguing enigmas surrounding the Great Pyramids of Giza is the conspicuous absence of historical records or depictions related to their construction. Unlike many ancient structures that have left behind detailed inscriptions, drawings, or artistic representations, the Great Pyramids remain enshrouded in silence.
Their construction techniques, purpose, and the identities of the architects and labor force behind them remain subjects of conjecture and mystery. This absence of concrete records adds to the mystique and allure of the pyramids, prompting questions about the extent of knowledge and technology possessed by the ancient Egyptians.
Atop the Geographical Center of the Earth
In a remarkable alignment with the Earth’s geography, the Great Pyramid is situated on the top of what is considered the geographical center of the planet. This geographical center holds significance as it serves as a reference point for the distribution of the earth’s mass. The precise positioning of the pyramid atop this geographical focal point has sparked discussions about the intentions and knowledge of the ancient pyramid builders. This alignment underscores the meticulous planning and astronomical awareness exhibited in the construction of these iconic structures. Travel essentials, accessories, kit & items on Amazon
The Miracles of the Casing Stones
The construction of the pyramids at Giza was marked by an ingenious architectural feature—the use of casing stones. These casing stones, meticulously crafted from polished limestone, adorned the entire exterior of the pyramids. The exceptional smoothness and precision of these stones are a testament to the advanced engineering capabilities of the ancient builders.
These stones played a crucial role in the pyramid’s interaction with sunlight. As the sun’s rays graced these polished surfaces, they would reflect and refract the light, creating a mesmerizing brilliance. This radiant quality led the Egyptians to affectionately refer to the pyramids as “Ikhet,” signifying “glory light.”
A Huge Door for Entry
The Great Pyramid stands as a unique architectural marvel among the pyramids of Giza. It features not one but three colossal swivel doors—a remarkable engineering feat. Despite each door weighing approximately 20 tons, they were ingeniously balanced to allow for effortless opening from the inside, requiring just a single hand. This architectural detail continues to captivate observers, highlighting the ancient builders’ profound understanding of mechanics and construction techniques. Free and Paid TRAVEL RESOURCES You May Explore
On the West Side of the Longest River
The Pyramid Complex at Giza occupies a strategic location on the west bank of the Nile River, which holds the distinction of being the longest river in the world. This geographical positioning adds to the historical and symbolic significance of the pyramids, as the Nile River was a lifeline for ancient Egyptian civilization, providing sustenance and fertility to the land. This connection between the pyramids and the Nile River underscores the deep-rooted relationship between the pharaohs’ tombs and the life-giving waters of the Nile.
Related Astronomy
The alignment of the Great Pyramid of Khufu, along with the other pyramids at Giza, has long been a subject of fascination and intrigue for astronomers and archaeologists. These pyramids are believed to be integrated with the constellation Orion, with their layout mirroring the positions of the stars in this celestial constellation. Find Destinations, Hotel, Flight, Accommodation, Pickup
This cosmic connection adds an intriguing layer of symbolism and significance to the pyramids, suggesting that they may have served not only as tombs for pharaohs but also as celestial markers or representations of the afterlife’s cosmic journey.
Wall Around France
To appreciate the monumental scale of the Great Pyramid, one can contemplate the sheer volume of its casing stones. These stones, when combined, amount to an astonishing height of around 2 feet and a formidable thickness of approximately 1 foot. This abundance of stone material would be sufficient to construct a protective wall encompassing the entire nation of France. Such comparisons highlight the magnitude of the ancient builders’ endeavors, as they labored to create an enduring testament to human achievement and architectural prowess. aRes Travel: Discounted Vacation packages & Travel Planning
The Arabs Break into the Pyramid
In the historical annals of 820 AD, an event of significance occurred when Arab forces breached the interior of the Great Pyramid. Upon entering, they encountered an austere environment. The most prominent feature within the pyramid’s depths was an empty granite box located in the King’s Chamber, often referred to as a sarcophagus.
Unfortunately, the Arab intruders caused damage to this enigmatic artifact, which was believed to have once cradled the remains of a pharaoh. Additionally, some of the pyramid’s stones were appropriated for the construction of a nearby mosque, marking a transformative moment in the pyramid’s evolving narrative. Track All of Your Travel Requirements from One Place.
UNESCO World Heritage Site
In recognition of their profound historical and cultural significance, the entire complex encompassing the Great Pyramid of Giza was accorded the prestigious status of a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1979. This distinction underscored the enduring legacy and global importance of these iconic structures. The UNESCO designation reaffirmed the pyramids’ status as treasures of humanity, transcending geographical boundaries and representing a shared heritage that continues to captivate and inspire. Kyte: Rental Cars On Demand. Delivered To Your Door
Final thoughts
In our contemporary era, the Great Pyramid of Giza continues to gleam resplendent in its grandeur—a living testament to the indomitable spirit and ingenious engineering prowess of ancient Egypt. It serves as a vivid embodiment of Egypt’s rich tapestry of history and cultural heritage, extending an open invitation to knowledge seekers and adventure enthusiasts from every corner of our diverse planet. It beckons them to revel in its enduring glory and embark on the enthralling journey of unraveling the mystique that it so steadfastly guards.
More Interesting Articles
- List of Caribbean Countries’ Flags and Their Capitals
- List of Scandinavian Countries – Capitals | Flags | Nordic
- Flags of Latin American Countries – Capitals | Population | Economy
- List, Capitals, and Flags of South American Countries
- Flags of North American Countries in Alphabetical Order
- Oceania Countries and Flags in Alphabetical Order
- Nordic Countries List – Capital | Flags | Population | Area
- List of Caribbean Countries in Alphabetical Order
- All-State Flags of the United States of America – Pictures | Images
- Alphabetical Order Flags of African Countries and Their Names
- All South Asian Countries’ Flags with Names
- Southeast Asian Countries and Their Flags
- Individual National Flags of Asian Countries with Names
- National Flags of European Countries with Names
- Names of Countries Flags – Flags of the World with Names
- Country Code List – Alpha-2 | Alpha-3 | Numeric | Phone
- US National Holidays – List of Holidays in America
- United States Embassies and Consulates – List with Link
- Time Zones List by Country – World Time | UTC | GMT | standard
- 2 Letter Country Codes – ISO 2-Digit Alpha Abbreviation



