United Nations Facts
United Nations facts at a glance |
|
| Headquarters | 760 United Nations Plaza New York City (international territory) |
|---|---|
| Official languages |
|
| Type | Intergovernmental organization |
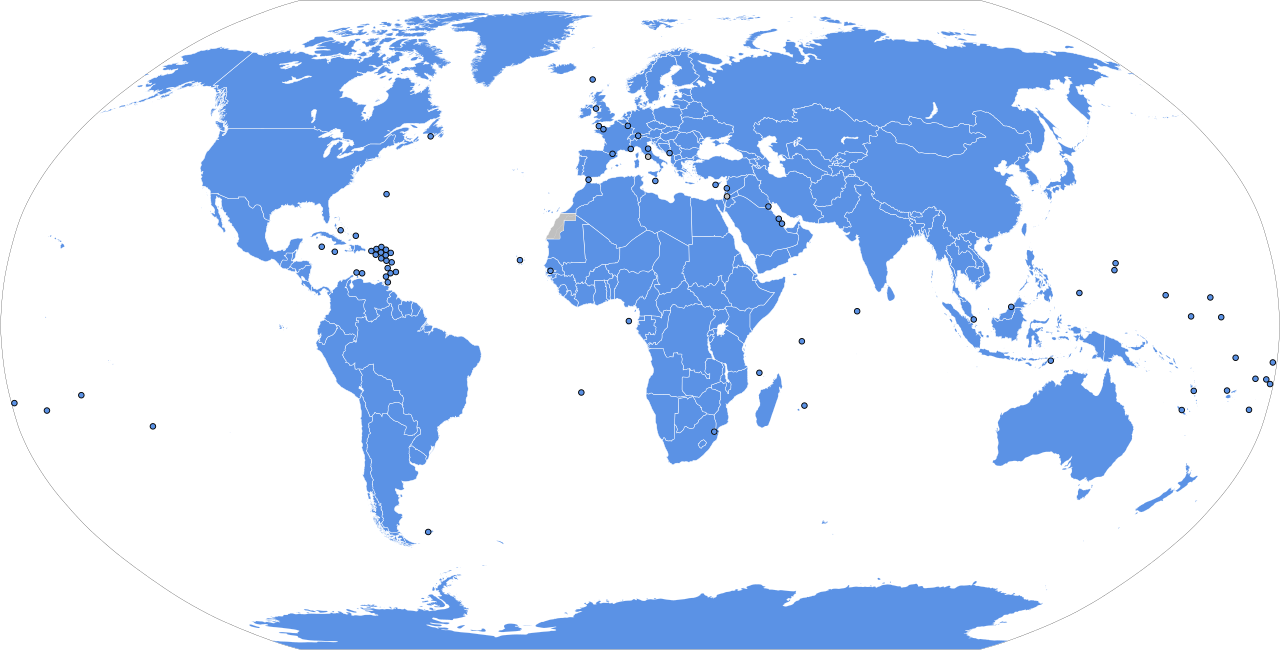
| Membership | 193 member states 2 observer states |
| Leaders | |
|
• Secretary‑General
|
António Guterres |
|
• Deputy Secretary-General
|
Amina J. Mohammed |
|
• General Assembly President
|
Volkan Bozkır |
|
• Economic and Social Council President
|
Munir Akram |
|
• Security Council President
|
Vasily Nebenzya (Russia) |
| Establishment | |
|
• UN Charter signed
|
26 June 1945 |
|
• Charter entered into force
|
24 October 1945 |
1. Genesis of the United Nations
United Nations has some important days there are interesting facts about the United Nations day.
17. The Core Entities of the United Nations
The intricate framework of the United Nations revolves around five fundamental entities, each playing a pivotal role in the global arena. These entities are the Economic and Social Council, the Security Council, the International Court of Justice, the UN Secretariat, and the UN General Assembly. Each of these components serves as a unique pillar, contributing to the multifaceted structure of the United Nations.
18. Post-World War II Genesis
The genesis of the United Nations traces back to the aftermath of the Second World War, a tumultuous period that reshaped the global landscape. It emerged as a response to the inadequacies of its predecessor, the League of Nations, which faltered in preventing the ravages of war. The formation of the UN stands as a testament to the international community’s collective resolve to foster cooperation and prevent future conflicts. This historical context adds depth to the understanding of the UN’s mission and purpose.
| No. | Name | Country of origin | Took office | Left office | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Trygve Lie | 2 February 1946 | 10 November 1952 | Resigned | |
| 2 | Dag Hammarskjöld | 10 April 1953 | 18 September 1961 | Died in office | |
| 3 | U Thant | 30 November 1961 | 31 December 1971 | First non-European to hold office | |
| 4 | Kurt Waldheim | 1 January 1972 | 31 December 1981 | ||
| 5 | Javier Pérez de Cuéllar | 1 January 1982 | 31 December 1991 | ||
| 6 | Boutros Boutros-Ghali | 1 January 1992 | 31 December 1996 | Served for the shortest time | |
| 7 | Kofi Annan | 1 January 1997 | 31 December 2006 | ||
| 8 | Ban Ki-moon | 1 January 2007 | 31 December 2016 | ||
| 9 | António Guterres | 1 January 2017 | Incumbent |
| No. | Acronym | Agency | Headquarters | Head | Established in |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | FAO | Food and Agriculture Organization | 1945 | ||
| 2 | IAEA | International Atomic Energy Agency | 1957 | ||
| 3 | ICAO | International Civil Aviation Organization | 1947 | ||
| 4 | IFAD | International Fund for Agricultural Development | 1977 | ||
| 5 | ILO | International Labour Organization | 1946 (1919) | ||
| 6 | IMO | International Maritime Organization | 1948 | ||
| 7 | IMF | International Monetary Fund | 1945 (1944) | ||
| 8 | ITU | International Telecommunication Union | 1947 (1865) | ||
| 9 | UNESCO | United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization | 1946 | ||
| 10 | UNIDO | United Nations Industrial Development Organization | 1967 | ||
| 11 | UNWTO | World Tourism Organization | 1974 | ||
| 12 | UPU | Universal Postal Union | 1947 (1874) | ||
| 13 | WBG | World Bank Group | 1945 (1944) | ||
| 14 | WFP | World Food Programme | 1963 | ||
| 15 | WHO | World Health Organization | 1948 | ||
| 16 | WIPO | World Intellectual Property Organization | 1974 | ||
| 17 | WMO | World Meteorological Organization | 1950 (1873) |
| Member state | Contribution (% of the UN budget) |
|---|---|
|
22.000
|
|
|
12.005
|
|
|
8.564
|
|
|
6.090
|
|
|
4.567
|
|
|
4.427
|
|
|
3.307
|
|
|
2.948
|
|
|
2.734
|
|
|
2.405
|
|
|
2.267
|
|
|
2.210
|
|
|
2.146
|
|
|
1.371
|
|
|
1.356
|
|
|
1.292
|
|
|
1.172
|
|
|
1.151
|
|
|
0.915
|
|
|
0.906
|
|
|
0.834
|
|
|
0.821
|
|
|
0.802
|
|
|
0.788
|
|
|
0.754
|
|
| Other member states |
12.168
|
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/United_Nations
Basic facts about the United Nations 42nd edition pdf: https://www.un.org/en/yearbook/article/basic-facts-about-united-nations
| Member state | Date of admission |
|---|---|
| 19 November 1946 | |
| 14 December 1955 | |
| 8 October 1962 | |
| 28 July 1993 | |
| 1 December 1976 | |
| 11 November 1981 | |
| 24 October 1945 | |
| 2 March 1992 | |
| 1 November 1945 | |
| 14 December 1955 | |
| 2 March 1992 | |
| 18 September 1973 | |
| 21 September 1971 | |
| 17 September 1974 | |
| 9 December 1966 | |
| 24 October 1945 | |
| 27 December 1945 | |
| 25 September 1981 | |
| 20 September 1960 | |
| 21 September 1971 | |
| 14 November 1945 | |
| 22 May 1992 | |
| 17 October 1966 | |
| 24 October 1945 | |
| 21 September 1984 | |
| 14 December 1955 | |
| 20 September 1960 | |
| 18 September 1962 | |
| 16 September 1975 | |
| 14 December 1955 | |
| 20 September 1960 | |
| 9 November 1945 | |
| 20 September 1960 | |
| 20 September 1960 | |
| 24 October 1945 | |
| 24 October 1945 | |
| 5 November 1945 | |
| 12 November 1975 | |
| 20 September 1960 | |
| 2 November 1945 | |
| 20 September 1960 | |
| 22 May 1992 | |
| 24 October 1945 | |
| 20 September 1960 | |
| 19 January 1993 | |
| 17 September 1991 | |
| 20 September 1960 | |
| 24 October 1945 | |
| 20 September 1977 | |
| 18 December 1978 | |
| 24 October 1945 | |
| 21 December 1945 | |
| 24 October 1945 | |
| 24 October 1945 | |
| 12 November 1968 | |
| 28 May 1993 | |
| 17 September 1991 | |
| 24 September 1968 | |
| 13 November 1945 | |
| 13 October 1970 | |
| 14 December 1955 | |
| 24 October 1945 | |
| 20 September 1960 | |
| 21 September 1965 | |
| 31 July 1992 | |
| 18 September 1973 | |
| 8 March 1957 | |
| 25 October 1945 | |
| 17 September 1974 | |
| 21 November 1945 | |
| 12 December 1958 | |
| 17 September 1974 | |
| 20 September 1966 | |
| 24 October 1945 | |
| 17 December 1945 | |
| 14 December 1955 | |
| 19 November 1946 | |
| 30 October 1945 | |
| 28 September 1950 | |
| 24 October 1945 | |
| 21 December 1945 | |
| 14 December 1955 | |
| 11 May 1949 | |
| 14 December 1955 | |
| 18 September 1962 | |
| 18 December 1956 | |
| 14 December 1955 | |
| 2 March 1992 | |
| 16 December 1963 | |
| 14 September 1999 | |
| 14 May 1963 | |
| 2 March 1992 | |
| 14 December 1955 | |
| 17 September 1991 | |
| 24 October 1945 | |
| 17 October 1966 | |
| 2 November 1945 | |
| 14 December 1955 | |
| 18 September 1990 | |
| 17 September 1991 | |
| 24 October 1945 | |
| 20 September 1960 | |
| 1 December 1964 | |
| 17 September 1957 | |
| 21 September 1965 | |
| 28 September 1960 | |
| 1 December 1964 | |
| 17 September 1991 | |
| 27 October 1961 | |
| 24 April 1968 | |
| 7 November 1945 | |
| 17 September 1991 | |
| 28 May 1993 | |
| 27 October 1961 | |
| 28 June 2006 | |
| 12 November 1956 | |
| 16 September 1975 | |
| 19 April 1948 | |
| 23 April 1990 | |
| 14 September 1999 | |
| 14 December 1955 | |
| 10 December 1945 | |
| 24 October 1945 | |
| 24 October 1945 | |
| 20 September 1960 | |
| 7 October 1960 | |
| 8 April 1993 | |
| 27 November 1945 | |
| 7 October 1971 | |
| 30 September 1947 | |
| 15 December 1994 | |
| 13 November 1945 | |
| 10 October 1975 | |
| 24 October 1945 | |
| 31 October 1945 | |
| 24 October 1945 | |
| 24 October 1945 | |
| 14 December 1955 | |
| 21 September 1971 | |
| 17 September 1991 | |
| 2 March 1992 | |
| 14 December 1955 | |
| 24 October 1945 | |
| 18 September 1962 | |
| 23 September 1983 | |
| 18 September 1979 | |
| 16 September 1980 | |
| 15 December 1976 | |
| 2 March 1992 | |
| 16 September 1975 | |
| 24 October 1945 | |
| 28 September 1960 | |
| 1 November 2000 | |
| 21 September 1976 | |
| 27 September 1961 | |
| 21 September 1965 | |
| 19 January 1993 | |
| 22 May 1992 | |
| 19 September 1978 | |
| 20 September 1960 | |
| 7 November 1945 | |
| 14 July 2011 | |
| 14 December 1955 | |
| 14 December 1955 | |
| 12 November 1956 | |
| 4 December 1975 | |
| 19 November 1946 | |
| 10 September 2002 | |
| 24 October 1945 | |
| 2 March 1992 | |
| 16 December 1946 | |
| 27 September 2002 | |
| 20 September 1960 | |
| 14 September 1999 | |
| 18 September 1962 | |
| 12 November 1956 | |
| 24 October 1945 | |
| 2 March 1992 | |
| 5 September 2000 | |
| 25 October 1962 | |
| 24 October 1945 | |
| 9 December 1971 | |
| 24 October 1945 | |
| 14 December 1961 | |
| 24 October 1945 | |
| 18 December 1945 | |
| 2 March 1992 | |
| 15 September 1981 | |
| 15 November 1945 | |
| 20 September 1977 | |
| 30 September 1947 | |
| 1 December 1964 | |
| 25 August 1980 |
Source: Wikipedia: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Member_states_of_the_United_Nations
More Interesting Articles
- 25 California Drought Facts – Causes | Effects | Solution
- 38 Interesting Facts About Australian Flag
- 25 Interesting Facts About The Roman Empire
- 100 Fun Facts About France One Should Know
- 15 Facts About Letchworth State Park, NY
- 40 Amazing Walt Disney World Facts
- 25 Interesting Facts About Glastonbury Festival
- 10 Interesting Facts About Antalya Turkey
- 70 Interesting Facts about the Eiffel Tower
- 26 Facts About Tokyo Meiji Jingu Temple
- 20 Fun Facts about Yosemite National Park, California
- 30 Interesting Facts About Dublin, Ireland
- 57 Must-do Things in Budapest for Travelers
- 13 Interesting Beijing Facts Everyone Must Know
- 16 Facts – Harbin International Ice and Snow Sculpture Festival
- 20 Surprising Facts About The German Flag
- 25 Surprising Facts About Florida Flag
- 17 Interesting Netherlands Facts to Surprise All
- 100 Tallest Completed Buildings in the World
- 15 Interesting Louvre Museum Facts to Know